Merging cells in Excel VBA can be a useful skill to have, especially when working with reports or dashboards where formatting is crucial. There are several ways to merge cells in Excel VBA, each with its own set of benefits and limitations. In this article, we will explore five different methods for merging cells in Excel VBA.
The Importance of Merging Cells in Excel VBA
Merging cells in Excel VBA is an essential skill for any VBA developer or Excel power user. By merging cells, you can create a single cell that spans multiple rows and columns, making it easier to format and analyze your data. Merging cells can also help to improve the readability of your spreadsheets by reducing the number of separate cells and making it easier to focus on the most important data.
Method 1: Using the MergeCells Method
The MergeCells method is the most straightforward way to merge cells in Excel VBA. This method allows you to specify the range of cells to merge and whether to merge them horizontally, vertically, or both.
Sub MergeCellsExample()
' Declare variables
Dim rng As Range
' Set range to merge
Set rng = Range("A1:C3")
' Merge cells
rng.MergeCells = True
' Optional: specify merge type
' rng.MergeCells = xlMergeAcross
' rng.MergeCells = xlMergeDown
End Sub
Method 2: Using the Union Method
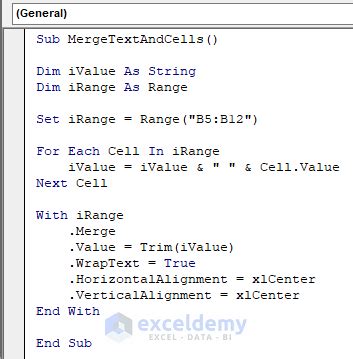
The Union method allows you to merge multiple ranges of cells into a single range. This method is useful when you need to merge cells that are not contiguous.
Sub MergeCellsUnionExample()
' Declare variables
Dim rng1 As Range
Dim rng2 As Range
Dim rng3 As Range
' Set ranges to merge
Set rng1 = Range("A1:C3")
Set rng2 = Range("E1:G3")
Set rng3 = Range("I1:K3")
' Merge cells using Union
Dim mergedRange As Range
Set mergedRange = Union(rng1, rng2, rng3)
mergedRange.MergeCells = True
End Sub
Method 3: Using the Areas Method
The Areas method allows you to merge multiple areas of a range into a single range. This method is useful when you need to merge cells that are separated by blank rows or columns.
Sub MergeCellsAreasExample()
' Declare variables
Dim rng As Range
' Set range to merge
Set rng = Range("A1:C3, E1:G3, I1:K3")
' Merge cells using Areas
Dim area As Range
For Each area In rng.Areas
area.MergeCells = True
Next area
End Sub
Method 4: Using the Resize Method
The Resize method allows you to resize a range to merge cells. This method is useful when you need to merge cells that are not contiguous.
Sub MergeCellsResizeExample()
' Declare variables
Dim rng As Range
' Set range to merge
Set rng = Range("A1")
' Merge cells using Resize
rng.Resize(3, 3).MergeCells = True
End Sub
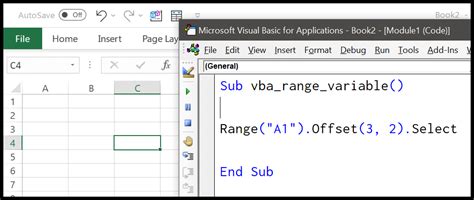
Method 5: Using the Offset Method
The Offset method allows you to offset a range to merge cells. This method is useful when you need to merge cells that are not contiguous.
Sub MergeCellsOffsetExample()
' Declare variables
Dim rng As Range
' Set range to merge
Set rng = Range("A1")
' Merge cells using Offset
rng.Offset(0, 1).Resize(3, 3).MergeCells = True
End Sub
Gallery of Merging Cells in Excel VBA
Merging Cells in Excel VBA Image Gallery
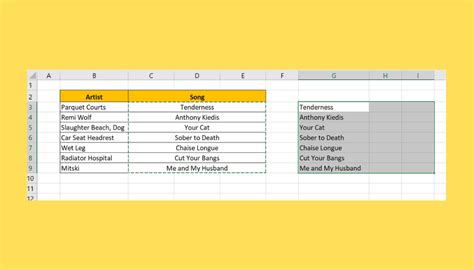
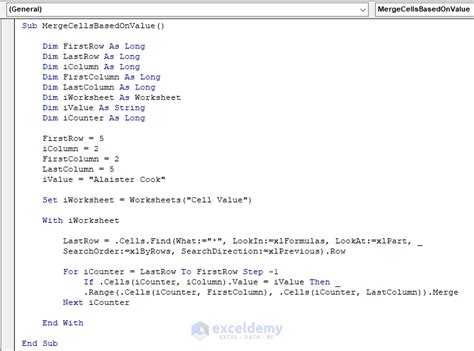
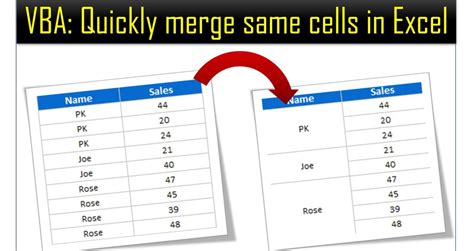
In conclusion, merging cells in Excel VBA is a useful skill to have, and there are several ways to do it. By using the MergeCells method, Union method, Areas method, Resize method, or Offset method, you can merge cells in a way that suits your needs. Remember to always test your code and adjust it as necessary to ensure that it works correctly in your specific situation. Happy coding!
We hope this article has been helpful in teaching you how to merge cells in Excel VBA. If you have any questions or need further assistance, please don't hesitate to ask.
