Intro
Explore Atrophic Vulvovaginitis pictures, symptoms, and treatments, understanding vaginal atrophy, vulvar dryness, and menopause-related changes, with informative images and expert insights.
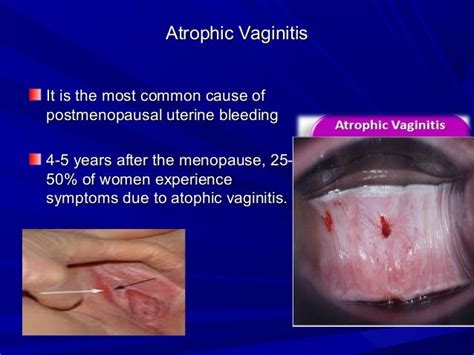
Atrophic vulvovaginitis is a condition that affects many women, especially during menopause or after childbirth. It is characterized by thinning, drying, and inflammation of the vaginal walls, which can cause discomfort, pain, and other symptoms. Understanding this condition is crucial for women to seek proper treatment and alleviate their symptoms. In this article, we will delve into the world of atrophic vulvovaginitis, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
Atrophic vulvovaginitis is a common condition that affects millions of women worldwide. It is estimated that up to 40% of postmenopausal women experience some degree of vaginal atrophy, which can significantly impact their quality of life. The condition is not only limited to menopausal women but can also affect women who have undergone hysterectomies, are breastfeeding, or have certain medical conditions. The symptoms of atrophic vulvovaginitis can vary from woman to woman but often include vaginal dryness, itching, burning, and pain during intercourse.
The causes of atrophic vulvovaginitis are multifactorial. Decreased estrogen levels are the primary cause of vaginal atrophy, which can occur during menopause, after childbirth, or due to certain medical conditions. Other factors that can contribute to the development of atrophic vulvovaginitis include smoking, certain medications, and a lack of sexual activity. Understanding the causes of atrophic vulvovaginitis is essential for developing effective treatment strategies.
Understanding Atrophic Vulvovaginitis
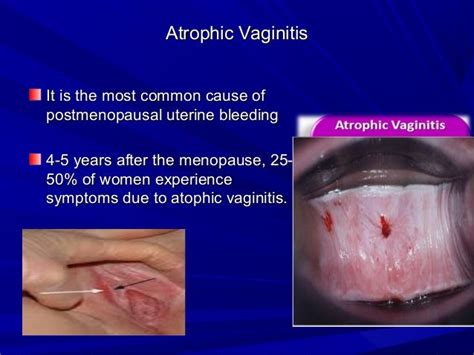
Atrophic vulvovaginitis is a complex condition that requires a comprehensive approach to diagnosis and treatment. A thorough medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests are necessary to diagnose atrophic vulvovaginitis. The diagnosis is often based on the presence of symptoms, such as vaginal dryness, itching, and pain, as well as the results of a pelvic examination. Laboratory tests, such as a vaginal smear or biopsy, may be performed to rule out other conditions.
Symptoms of Atrophic Vulvovaginitis
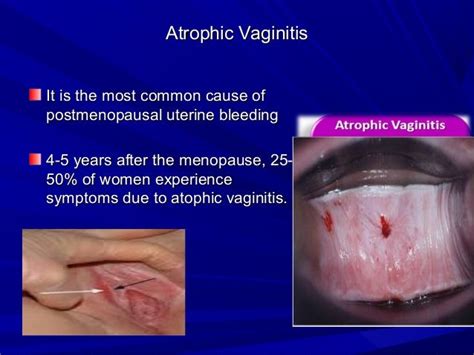
The symptoms of atrophic vulvovaginitis can vary from woman to woman but often include:
- Vaginal dryness
- Itching or burning sensations
- Pain during intercourse
- Discharge or bleeding
- Urinary frequency or urgency
- Painful urination
These symptoms can significantly impact a woman's quality of life, making it essential to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time.
Causes of Atrophic Vulvovaginitis

The causes of atrophic vulvovaginitis are multifactorial. Decreased estrogen levels are the primary cause of vaginal atrophy, which can occur during menopause, after childbirth, or due to certain medical conditions. Other factors that can contribute to the development of atrophic vulvovaginitis include:
- Smoking
- Certain medications
- Lack of sexual activity
- Hysterectomy
- Breastfeeding
- Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes or thyroid disorders
Understanding the causes of atrophic vulvovaginitis is essential for developing effective treatment strategies.
Diagnosis of Atrophic Vulvovaginitis

The diagnosis of atrophic vulvovaginitis is based on a thorough medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests. The diagnosis is often based on the presence of symptoms, such as vaginal dryness, itching, and pain, as well as the results of a pelvic examination. Laboratory tests, such as a vaginal smear or biopsy, may be performed to rule out other conditions.
Treatment Options for Atrophic Vulvovaginitis

The treatment options for atrophic vulvovaginitis depend on the severity of symptoms and the underlying cause of the condition. Treatment options may include:
- Hormone replacement therapy (HRT)
- Vaginal estrogen therapy
- Lubricants and moisturizers
- Pain relief medications
- Lifestyle changes, such as increasing sexual activity or quitting smoking
It is essential to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of treatment for atrophic vulvovaginitis.
Prevention of Atrophic Vulvovaginitis
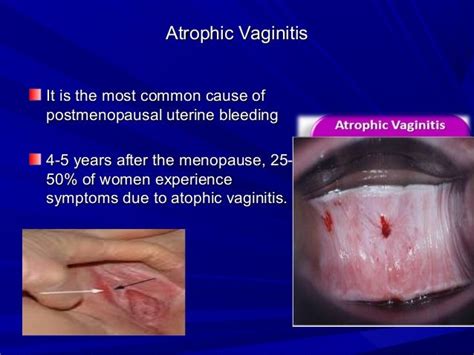
Preventing atrophic vulvovaginitis is crucial for maintaining vaginal health. Prevention strategies may include:
- Practicing safe sex
- Using lubricants during intercourse
- Avoiding smoking
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Engaging in regular exercise
- Eating a balanced diet
By following these prevention strategies, women can reduce their risk of developing atrophic vulvovaginitis.
Gallery of Atrophic Vulvovaginitis
Atrophic Vulvovaginitis Image Gallery
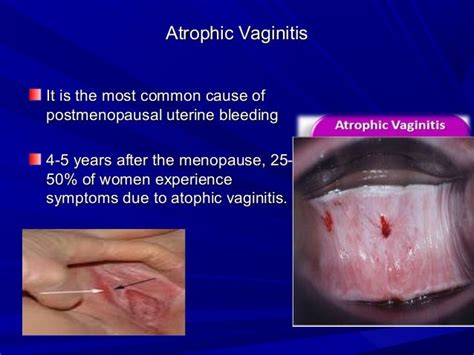
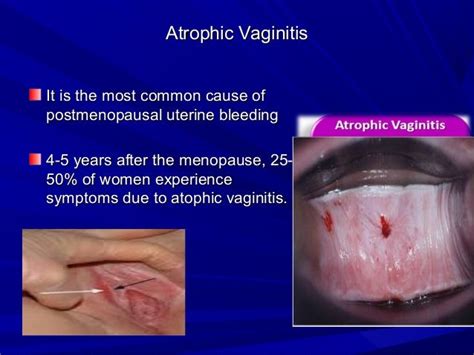




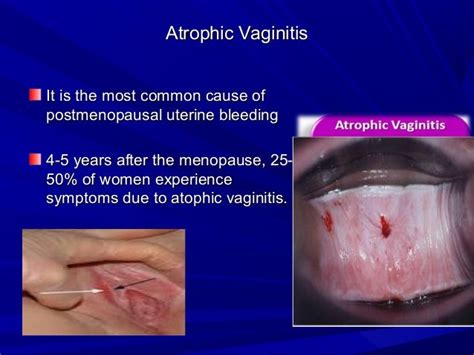
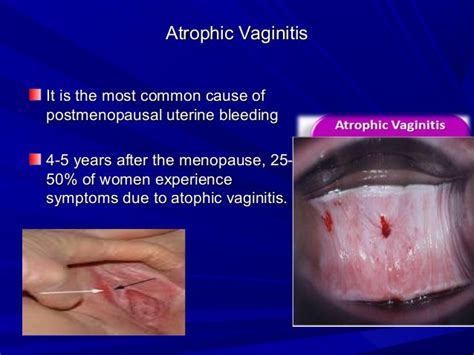
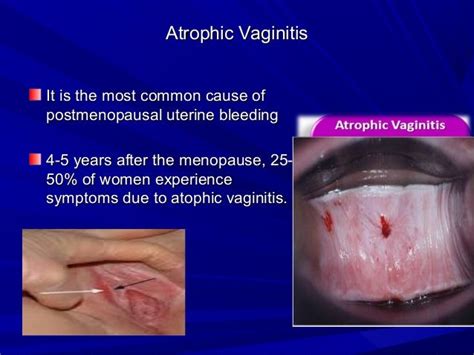
In conclusion, atrophic vulvovaginitis is a common condition that affects many women. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options is essential for managing the condition and improving quality of life. By following prevention strategies and seeking medical attention if symptoms persist, women can reduce their risk of developing atrophic vulvovaginitis. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with atrophic vulvovaginitis in the comments section below. If you found this article informative, please share it with your friends and family to help raise awareness about this important women's health issue.
