Intro
Discover Pulmonía causes, symptoms, and effects. Learn about respiratory infections, lung inflammation, and breathing difficulties, to understand this condition and its treatment options.
Pulmonía, commonly known as pneumonia, is a serious and potentially life-threatening infection that affects the lungs. It is a major public health concern worldwide, causing millions of deaths each year, particularly among vulnerable populations such as the elderly, young children, and people with compromised immune systems. Despite its severity, pneumonia is often misunderstood, and its symptoms can be mistaken for those of other respiratory infections. In this article, we will delve into the causes and symptoms of pulmonía, as well as its diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
Pulmonía is a complex disease that can be caused by a variety of factors, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microorganisms. The most common causes of pneumonia are Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Moraxella catarrhalis. These bacteria can spread through respiratory droplets, such as those produced by coughing or sneezing, or by touching contaminated surfaces. Viral pneumonia, on the other hand, is often caused by influenza, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and adenovirus. Fungal pneumonia is more common in people with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or undergoing chemotherapy.
The symptoms of pulmonía can vary depending on the cause and severity of the infection. Common symptoms include cough, fever, chills, shortness of breath, and chest pain. In severe cases, pneumonia can cause respiratory failure, sepsis, and even death. It is essential to seek medical attention immediately if you or a loved one is experiencing any of these symptoms.
Causes of Pulmonía
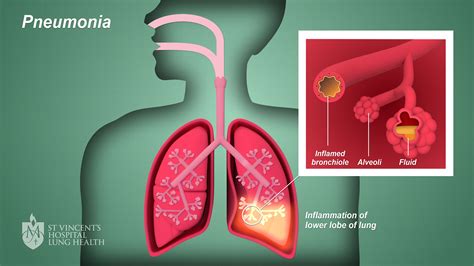
Types of Pulmonía
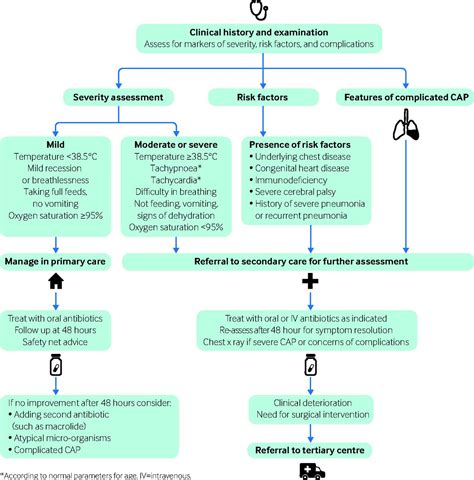
There are several types of pulmonía, each with distinct characteristics and causes. Community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) is the most common type, occurring in people who have not recently been hospitalized or exposed to healthcare-associated pathogens. Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) occurs in people who have been hospitalized for other conditions and are at risk of developing pneumonia due to their compromised immune systems or exposure to hospital-acquired pathogens. Ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP) occurs in people who are on mechanical ventilation, such as those in intensive care units.Symptoms of Pulmonía
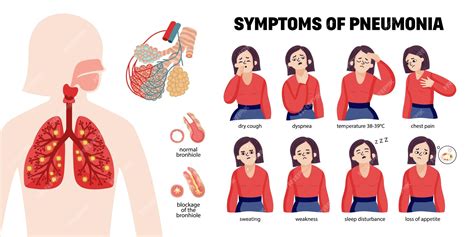
Diagnosis of Pulmonía
Diagnosing pulmonía can be challenging, as its symptoms can be similar to those of other respiratory infections. A physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests are essential for diagnosing pneumonia. Chest X-rays, blood tests, and sputum cultures can help identify the cause and severity of the infection.Treatment of Pulmonía
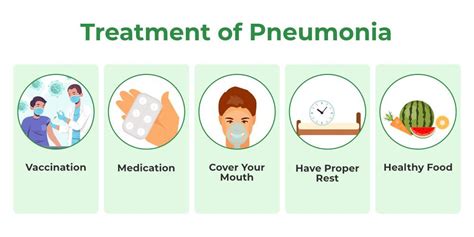
Prevention of Pulmonía
Preventing pulmonía is essential, particularly in vulnerable populations such as the elderly, young children, and people with compromised immune systems. Vaccinations, such as the pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV) and the influenza vaccine, can help prevent pneumonia. Practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands regularly and avoiding close contact with people who are sick, can also help prevent the spread of pneumonia.Complications of Pulmonía
Management of Pulmonía
Managing pulmonía requires a comprehensive approach that includes medical treatment, supportive care, and prevention. Medical treatment involves antibiotics, antiviral medications, or antifungal medications, depending on the cause of the infection. Supportive care includes oxygen therapy, mechanical ventilation, and hospitalization, if necessary. Prevention involves vaccinations, good hygiene, and avoiding close contact with people who are sick.Gallery of Pulmonía Images
Pulmonía Image Gallery
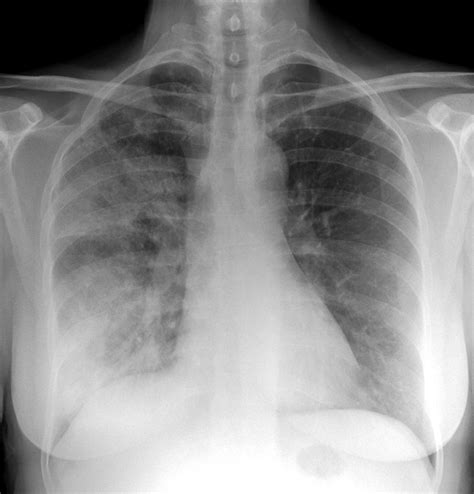
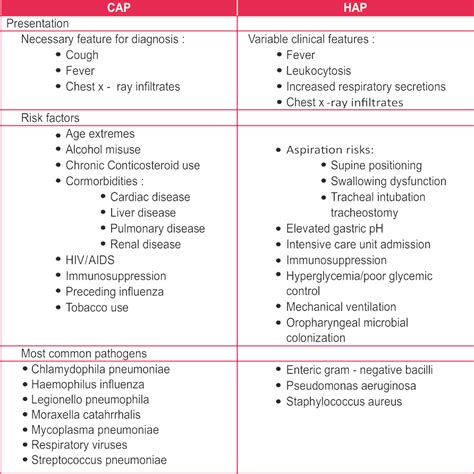

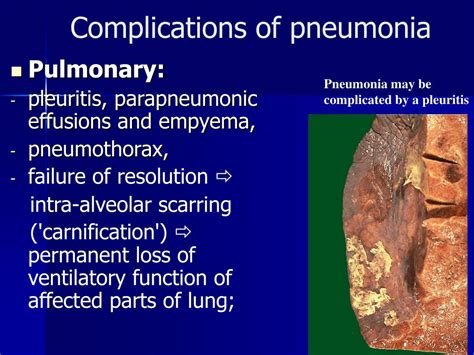


In conclusion, pulmonía is a serious and potentially life-threatening infection that affects the lungs. Its causes and symptoms can vary depending on the type of infection, and its diagnosis, treatment, and prevention require a comprehensive approach. By understanding the causes and symptoms of pulmonía, we can take steps to prevent its spread and manage its complications. If you or a loved one is experiencing symptoms of pulmonía, seek medical attention immediately. Share this article with others to raise awareness about pulmonía and its importance in public health. Comment below with your thoughts and questions, and let's work together to prevent the spread of this deadly infection.
