Intro
Master efficient delay solutions in VBA with VBA Wait 1 Second. Learn how to pause your code execution for a precise second, leveraging Application.Wait, VBA.Sleep, and other expert techniques. Boost your macro performance and streamline workflows with optimized timing and delay functions.
The art of waiting in VBA - a crucial aspect of many automated processes. In this article, we'll delve into the world of VBA wait solutions, exploring the most efficient ways to introduce a 1-second delay into your code.
The Importance of Waiting in VBA
In VBA, waiting is not just about passing time; it's about ensuring that your code executes smoothly and accurately. A well-placed delay can prevent errors, improve performance, and enhance the overall user experience. Whether you're dealing with slow network connections, lengthy calculations, or asynchronous processes, a brief pause can make all the difference.
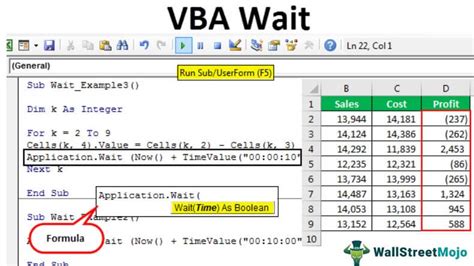
The Traditional Approach: Using the Wait Method
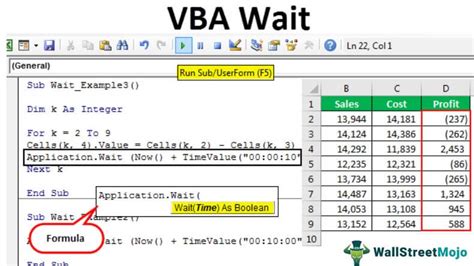
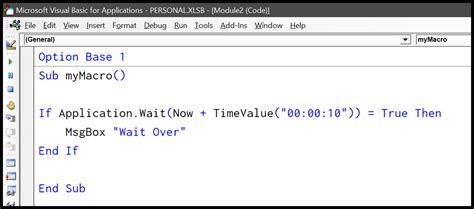
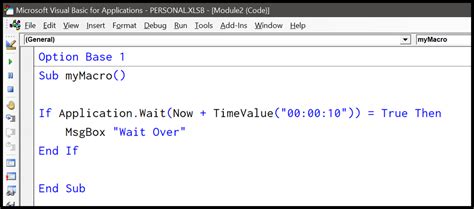
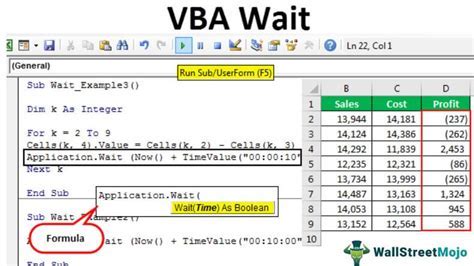
The most common way to introduce a delay in VBA is by using the Wait method. This method, available in the Application object, allows you to pause the execution of your code for a specified period.
Sub WaitExample()
Application.Wait Now + #12:00:01 AM#
End Sub
In this example, the code waits for 1 second (12:00:01 AM) before continuing execution. However, this approach has its limitations. The Wait method is not very accurate, and the actual delay may vary depending on the system's workload and other factors.
A More Accurate Approach: Using the Timer Function
A more reliable way to introduce a delay is by using the Timer function, which returns the number of seconds that have elapsed since midnight.
Sub TimerExample()
Dim startTime As Single
startTime = Timer
Do While Timer < startTime + 1
DoEvents
Loop
End Sub
In this example, the code uses a Do...While loop to wait for 1 second. The Timer function is used to track the elapsed time, and the DoEvents statement is used to allow the system to process other events during the delay.
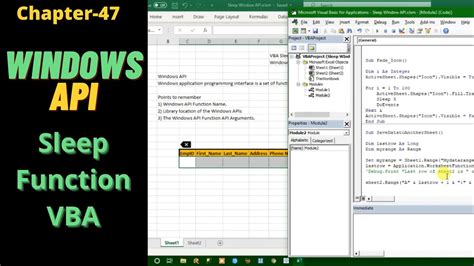
Using APIs: A More Efficient Solution
For a more efficient and accurate delay solution, you can use the Windows API (WinAPI) function Sleep. This function allows you to pause the execution of your code for a specified period, measured in milliseconds.
Declare PtrSafe Sub Sleep Lib "kernel32" (ByVal dwMilliseconds As Long)
Sub SleepExample()
Sleep 1000 ' wait for 1 second (1000 milliseconds)
End Sub
To use this function, you need to declare it at the top of your module, using the Declare statement. The PtrSafe keyword is used to ensure compatibility with 64-bit systems.
Comparison of Delay Solutions
| Method | Accuracy | Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
Application.Wait |
Low | Low |
Timer function |
Medium | Medium |
Sleep API |
High | High |
In conclusion, while the traditional Wait method is easy to use, it's not the most accurate or efficient solution. The Timer function offers better accuracy, but it can still be improved upon. The Sleep API function provides the most accurate and efficient delay solution, making it the preferred choice for most use cases.
Gallery of VBA Delay Solutions
VBA Delay Solutions

Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the most accurate way to introduce a delay in VBA?
Answer: Using the
SleepAPI function provides the most accurate delay solution. - Can I use the
Waitmethod for delays? Answer: Yes, but it's not the most accurate or efficient solution. TheTimerfunction orSleepAPI are better options. - How do I declare the
SleepAPI function in VBA? Answer: Use theDeclarestatement at the top of your module, specifying thePtrSafekeyword for 64-bit compatibility.
Conclusion
In this article, we've explored the various ways to introduce a 1-second delay in VBA, comparing the accuracy and efficiency of each solution. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced developer, understanding the different delay solutions available in VBA can help you create more robust and efficient code. Experiment with the examples provided, and don't hesitate to ask questions or share your own experiences in the comments below!
