Intro
Discover the world of job manufacturing, a crucial aspect of the broader manufacturing industry. Learn about the definition, processes, and significance of job manufacturing, including contract manufacturing, production planning, and workflow optimization. Explore how this industry supports various sectors, from aerospace to automotive, and drives economic growth.
Job manufacturing is a production process that involves creating a specific product or batch of products in response to a customer's order or demand. This approach differs from mass production, where a large quantity of products is produced without a specific order. In job manufacturing, each product or batch is unique and requires a customized production process.
The job manufacturing industry is a significant sector of the global economy, with applications in various fields, including aerospace, automotive, construction, and consumer goods. Companies that adopt job manufacturing strategies often focus on meeting specific customer requirements, reducing lead times, and improving product quality.
Types of Job Manufacturing
There are several types of job manufacturing, including:
- One-off production: This involves producing a single product or a small batch of products in response to a customer's order.
- Batch production: This involves producing a specific quantity of products in batches, often in response to a customer's order or forecasted demand.
- Custom production: This involves producing a customized product or batch of products that meet specific customer requirements.
- Engineer-to-order (ETO): This involves producing a product or batch of products that are designed and engineered to meet specific customer requirements.
Key Characteristics of Job Manufacturing
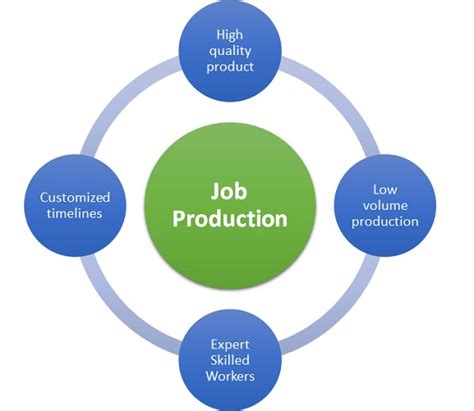
Job manufacturing has several key characteristics, including:
- Low volume: Job manufacturing typically involves producing small quantities of products.
- High variety: Job manufacturing often involves producing a wide range of products or product variations.
- Customization: Job manufacturing involves producing products that meet specific customer requirements.
- Flexibility: Job manufacturing requires flexibility in production processes and supply chains to respond to changing customer demands.
Benefits of Job Manufacturing
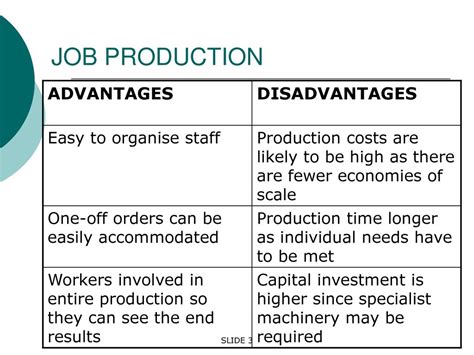
Job manufacturing offers several benefits, including:
- Improved customer satisfaction: Job manufacturing allows companies to produce products that meet specific customer requirements, leading to improved customer satisfaction.
- Reduced inventory levels: Job manufacturing involves producing products in response to customer orders, reducing the need for inventory storage.
- Increased flexibility: Job manufacturing allows companies to respond quickly to changing customer demands and market trends.
- Improved product quality: Job manufacturing involves producing products in small batches or one-off quantities, allowing for greater attention to detail and improved product quality.
Challenges of Job Manufacturing

Job manufacturing also presents several challenges, including:
- Higher production costs: Job manufacturing often involves higher production costs due to the need for customized production processes and lower economies of scale.
- Increased complexity: Job manufacturing involves managing a wide range of products and production processes, which can increase complexity and reduce efficiency.
- Reduced efficiency: Job manufacturing often involves producing products in small batches or one-off quantities, which can reduce efficiency and increase production times.
Industry Applications of Job Manufacturing

Job manufacturing has applications in various industries, including:
- Aerospace: Job manufacturing is used in the aerospace industry to produce customized aircraft and spacecraft components.
- Automotive: Job manufacturing is used in the automotive industry to produce customized vehicle components and aftermarket parts.
- Construction: Job manufacturing is used in the construction industry to produce customized building components and materials.
- Consumer goods: Job manufacturing is used in the consumer goods industry to produce customized products, such as furniture and electronics.
Technologies Used in Job Manufacturing

Several technologies are used in job manufacturing, including:
- Computer-aided design (CAD): CAD software is used to design and engineer customized products.
- Computer-aided manufacturing (CAM): CAM software is used to program and control production processes.
- 3D printing: 3D printing technology is used to produce customized products and components.
- Robotics: Robotics technology is used to automate production processes and improve efficiency.
Gallery of Job Manufacturing Images
Job Manufacturing Image Gallery








We hope this article has provided a comprehensive overview of job manufacturing, its benefits, challenges, and industry applications. As the manufacturing landscape continues to evolve, job manufacturing is likely to play an increasingly important role in meeting customer demands for customized products and services.
