Intro
Boost math skills with our Average Speed Worksheet, designed to simplify complex calculations. Master formulas, solve problems, and grasp concepts effortlessly. Calculate average speed, distance, and time with ease, using our worksheets tailored for students and educators. Enhance understanding of physics and math fundamentals with our comprehensive resources.
The concept of average speed is a fundamental aspect of physics and mathematics, used to calculate the mean rate of change of an object's position over a specific period. It is a crucial formula in understanding the movement of objects and has numerous real-world applications. However, many students find it challenging to grasp the concept and perform calculations accurately. In this article, we will delve into the world of average speed, exploring its significance, the formula, and providing practical examples to make calculations easier.
Understanding Average Speed
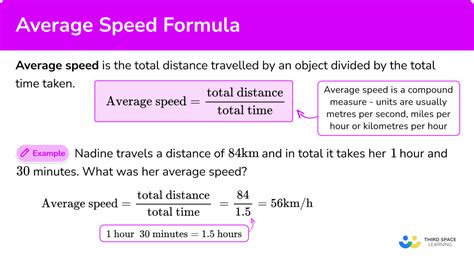
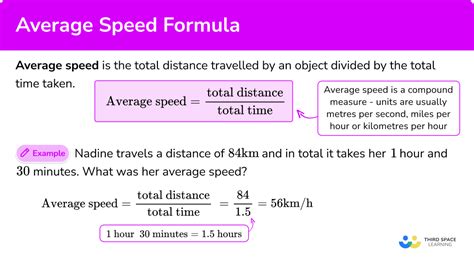
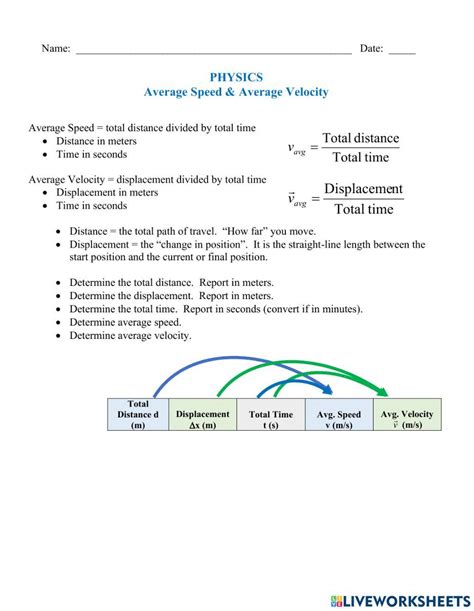
Average speed is a measure of the total distance traveled by an object divided by the total time taken to cover that distance. It is a scalar quantity, which means it has only magnitude and no direction. Average speed is used to describe the motion of an object over a specific period, and it is a crucial concept in understanding various real-world phenomena, such as traffic flow, sports, and even space exploration.
Why is Average Speed Important?
Average speed has numerous practical applications in various fields, including:
- Traffic management: Average speed is used to calculate the mean speed of vehicles on a particular road or highway, helping traffic managers to optimize traffic flow and reduce congestion.
- Sports: Average speed is used to measure the performance of athletes in various sports, such as running, cycling, and swimming.
- Space exploration: Average speed is used to calculate the speed of spacecraft and satellites, helping scientists to navigate and communicate with these objects.
The Average Speed Formula

The average speed formula is simple and straightforward:
Average Speed = Total Distance / Total Time
Mathematically, this can be represented as:
AS = Δx / Δt
Where: AS = Average Speed Δx = Total Distance Δt = Total Time
How to Calculate Average Speed
Calculating average speed is a simple process that involves dividing the total distance traveled by the total time taken. Here are the steps:
- Measure the total distance traveled by the object.
- Measure the total time taken to cover that distance.
- Divide the total distance by the total time to get the average speed.
Practical Examples
Let's consider a few practical examples to illustrate the concept of average speed:
Example 1: A car travels from City A to City B, covering a distance of 200 miles in 4 hours. What is the average speed of the car?
Solution: Average Speed = Total Distance / Total Time = 200 miles / 4 hours = 50 miles per hour
Example 2: A cyclist travels a distance of 20 kilometers in 1 hour. What is the average speed of the cyclist?
Solution: Average Speed = Total Distance / Total Time = 20 kilometers / 1 hour = 20 kilometers per hour
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When calculating average speed, there are a few common mistakes to avoid:
- Using the wrong units: Make sure to use the correct units for distance and time.
- Forgetting to convert units: If the units are different, make sure to convert them before performing the calculation.
- Rounding errors: Avoid rounding errors by using exact values for distance and time.
Conclusion
Average speed is a fundamental concept in physics and mathematics, used to calculate the mean rate of change of an object's position over a specific period. By understanding the formula and performing calculations accurately, you can gain a deeper understanding of various real-world phenomena. Remember to avoid common mistakes and use practical examples to make calculations easier. With practice and patience, you can master the concept of average speed and become proficient in performing calculations.
Gallery of Average Speed Calculations
Average Speed Calculations Image Gallery