Intro
Explore the key differences between the Constitution and Articles of Confederation, understanding federalism, sovereignty, and governance, to grasp the evolution of the US government system.
The United States of America has a rich history, and its development as a nation has been shaped by various documents and agreements. Two of the most significant documents in American history are the Constitution and the Articles of Confederation. While both documents played crucial roles in the formation and growth of the United States, they have distinct differences in terms of their purpose, structure, and impact on the country. In this article, we will delve into the importance of understanding the differences between the Constitution and the Articles of Confederation, and why this knowledge is essential for appreciating the foundations of American democracy.
The Constitution and the Articles of Confederation are two foundational documents that have shaped the course of American history. The Articles of Confederation, adopted in 1781, was the first attempt at creating a unified government for the newly independent states. However, it soon became apparent that this document had several limitations, leading to the drafting and adoption of the Constitution in 1787. The Constitution has since become the supreme law of the land, outlining the framework of the federal government and the relationship between the government and its citizens. Understanding the differences between these two documents is crucial for grasping the evolution of American politics and the principles that underpin the country's system of government.
The significance of studying the Constitution and the Articles of Confederation extends beyond mere historical interest. These documents have had a lasting impact on American society, shaping the country's political institutions, laws, and values. By examining the strengths and weaknesses of each document, we can gain insights into the challenges faced by the nation's founders and the trade-offs they made in creating a new system of government. Moreover, understanding the historical context and the key provisions of these documents can help us appreciate the complexities of American democracy and the ongoing debates about the role of government, individual rights, and federalism. As we explore the differences between the Constitution and the Articles of Confederation, we will see how these documents reflect the changing needs and aspirations of the American people.
Introduction to the Articles of Confederation

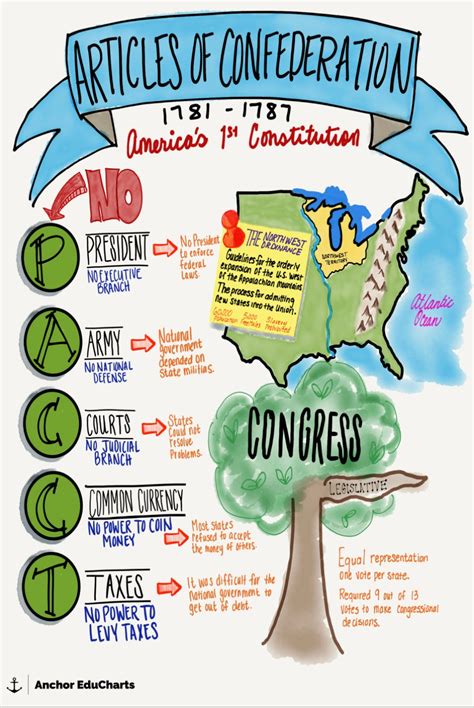
The Articles of Confederation was the first attempt at creating a unified government for the newly independent states. Adopted in 1781, this document established a loose alliance of states with a weak central government. The Articles of Confederation had several key features, including a unicameral Congress with limited powers, no executive or judicial branches, and a system of government that relied heavily on the cooperation of the states. While the Articles of Confederation provided a framework for cooperation among the states, it soon became apparent that this document had several limitations, including the lack of power to regulate commerce, enforce laws, or provide for national defense.
Limitations of the Articles of Confederation
The limitations of the Articles of Confederation became increasingly apparent as the young nation faced various challenges, including economic difficulties, territorial disputes, and external threats. The lack of a strong central government made it difficult to coordinate a unified response to these challenges, leading to a sense of disunity and fragmentation among the states. Moreover, the Articles of Confederation did not provide for a system of taxation, making it challenging for the government to raise revenue and fund its operations. These limitations ultimately led to the drafting and adoption of the Constitution, which aimed to create a more robust and effective system of government.Introduction to the Constitution

The Constitution, adopted in 1787, is the supreme law of the land, outlining the framework of the federal government and the relationship between the government and its citizens. The Constitution established a federal system of government, with three branches of government: the legislative, executive, and judicial. This system of government is designed to provide checks and balances, preventing any one branch from becoming too powerful. The Constitution also established the principles of federalism, which divides power between the federal government and the states. Additionally, the Constitution enshrines individual rights and freedoms, such as freedom of speech, assembly, and the press, which are essential to American democracy.
Key Provisions of the Constitution
The Constitution has several key provisions that have shaped the course of American history. The document establishes the principles of representation, with members of Congress elected by the people to represent their interests. The Constitution also provides for a system of taxation, allowing the government to raise revenue and fund its operations. Furthermore, the Constitution establishes the Supreme Court as the highest court in the land, with the power to interpret laws and ensure that they are consistent with the Constitution. These provisions, among others, have helped to create a stable and effective system of government, which has endured for over two centuries.Comparison of the Constitution and the Articles of Confederation
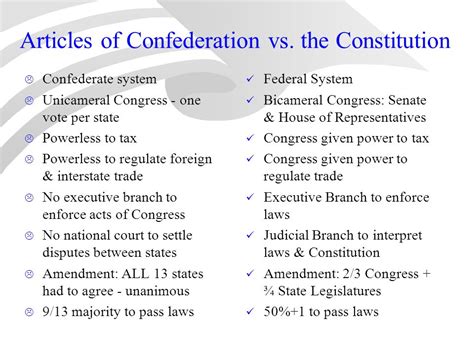
A comparison of the Constitution and the Articles of Confederation reveals significant differences in terms of their purpose, structure, and impact on the country. The Articles of Confederation was a loose alliance of states with a weak central government, while the Constitution established a federal system of government with three branches and a system of checks and balances. The Constitution also enshrines individual rights and freedoms, which are essential to American democracy. In contrast, the Articles of Confederation did not provide for individual rights, and the government relied heavily on the cooperation of the states. These differences reflect the changing needs and aspirations of the American people, as well as the lessons learned from the limitations of the Articles of Confederation.
Differences in Structure and Powers
The structure and powers of the government under the Constitution and the Articles of Confederation are significantly different. The Constitution establishes a federal system of government, with three branches of government: the legislative, executive, and judicial. In contrast, the Articles of Confederation had a unicameral Congress with limited powers, no executive or judicial branches, and a system of government that relied heavily on the cooperation of the states. The Constitution also provides for a system of representation, with members of Congress elected by the people to represent their interests. These differences in structure and powers have had a lasting impact on American politics, shaping the relationship between the government and its citizens.Impact of the Constitution and the Articles of Confederation

The Constitution and the Articles of Confederation have had a lasting impact on American society, shaping the country's political institutions, laws, and values. The Constitution has provided a framework for a stable and effective system of government, which has endured for over two centuries. The document has also enshrined individual rights and freedoms, which are essential to American democracy. In contrast, the Articles of Confederation had a more limited impact, as its limitations and weaknesses ultimately led to its replacement by the Constitution. However, the Articles of Confederation played an important role in the development of American politics, as it provided a framework for cooperation among the states and helped to establish the principles of federalism.
Legacy of the Constitution and the Articles of Confederation
The legacy of the Constitution and the Articles of Confederation can be seen in the ongoing debates about the role of government, individual rights, and federalism. The Constitution has provided a framework for a stable and effective system of government, which has endured for over two centuries. The document has also enshrined individual rights and freedoms, which are essential to American democracy. In contrast, the Articles of Confederation has served as a reminder of the limitations and weaknesses of a loose alliance of states with a weak central government. The legacy of these documents continues to shape American politics, as politicians, scholars, and citizens continue to debate the meaning and significance of the Constitution and the Articles of Confederation.Gallery of Constitution and Articles of Confederation
Constitution and Articles of Confederation Image Gallery









As we conclude our exploration of the Constitution and the Articles of Confederation, we are reminded of the significance of these documents in shaping American history and politics. The differences between these two documents reflect the changing needs and aspirations of the American people, as well as the lessons learned from the limitations of the Articles of Confederation. By understanding the importance of these documents, we can gain insights into the complexities of American democracy and the ongoing debates about the role of government, individual rights, and federalism. We invite our readers to share their thoughts and reflections on the Constitution and the Articles of Confederation, and to continue the conversation about the significance of these documents in American history and politics. Please feel free to comment, share this article, or take specific actions to learn more about these foundational documents and their enduring impact on American society.
