Intro
Unravel the mysteries of motion with our in-depth guide to the Distance vs Time Graph Worksheet. Learn how to interpret and analyze these graphs, understanding concepts like speed, velocity, and acceleration. Master the art of graphing distance-time relationships and solve real-world problems with ease.
Understanding distance vs time graphs is a fundamental concept in physics and mathematics. These graphs are used to visualize the relationship between the distance traveled by an object and the time it takes to travel that distance. In this article, we will delve into the world of distance vs time graphs, exploring what they are, how to read them, and provide a comprehensive worksheet to help you practice.
What is a Distance vs Time Graph?
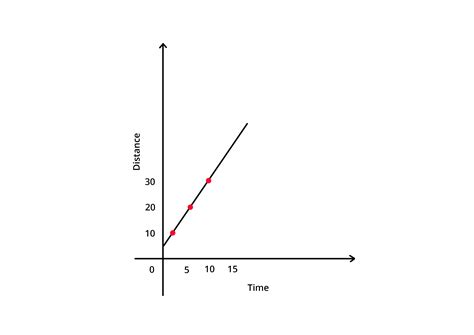
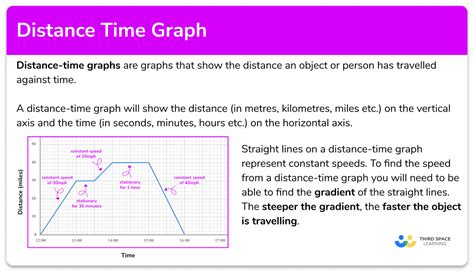
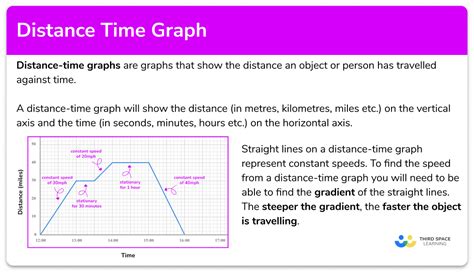
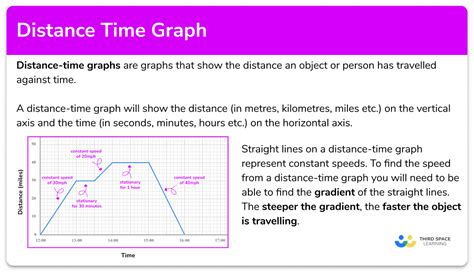
A distance vs time graph is a type of graph that shows the relationship between the distance traveled by an object and the time it takes to travel that distance. The graph has two axes: the x-axis represents time, and the y-axis represents distance. The graph is used to show how the distance traveled by an object changes over time.
Reading a Distance vs Time Graph
Reading a distance vs time graph is relatively straightforward. Here are the key things to look for:
- The x-axis represents time, and the y-axis represents distance.
- The graph shows the distance traveled by an object at different times.
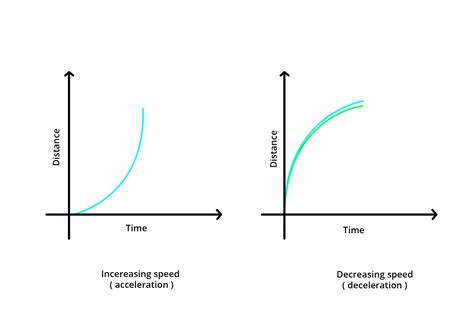
- The slope of the graph represents the speed of the object. A steeper slope indicates a faster speed, while a shallower slope indicates a slower speed.
- A horizontal line on the graph indicates that the object is stationary, while a vertical line indicates that the object is moving at an infinite speed.
Types of Distance vs Time Graphs
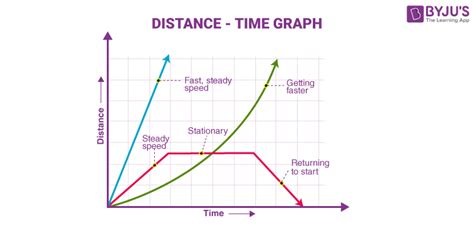
There are several types of distance vs time graphs, including:
- Linear graphs: These graphs show a straight line, indicating a constant speed.
- Non-linear graphs: These graphs show a curved line, indicating a changing speed.
- Step graphs: These graphs show a series of horizontal lines, indicating that the object is moving at a constant speed for a certain period of time.
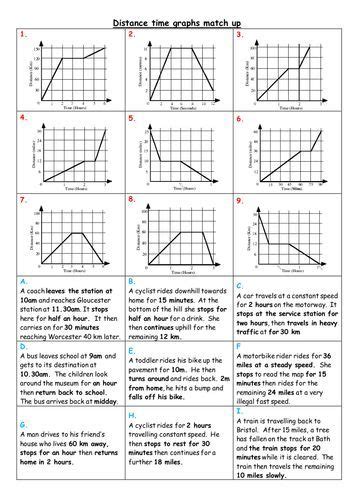
Worksheet: Distance vs Time Graphs
Now that we have covered the basics of distance vs time graphs, it's time to practice! Here is a comprehensive worksheet to help you test your understanding.
Question 1: A car travels from point A to point B in 2 hours. If the distance between point A and point B is 100 km, what is the average speed of the car?
Answer: 50 km/h
Question 2: A runner runs at a constant speed of 10 km/h for 3 hours. How far does the runner travel?
Answer: 30 km
Question 3: A car accelerates from rest to a speed of 60 km/h in 10 seconds. What is the acceleration of the car?
Answer: 6 m/s^2
Question 4: A bike travels at a constant speed of 20 km/h for 2 hours. What is the distance traveled by the bike?
Answer: 40 km
Distance vs Time Graphs: Real-World Applications
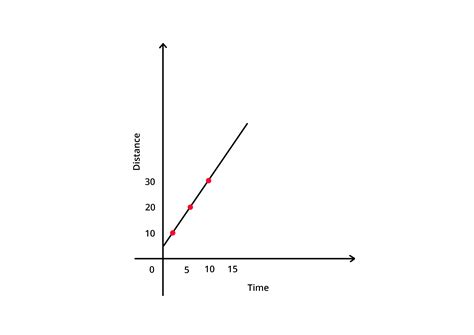
Distance vs time graphs have numerous real-world applications, including:
- Physics and engineering: Distance vs time graphs are used to analyze the motion of objects, including cars, planes, and trains.
- Transportation: Distance vs time graphs are used to plan routes and schedules for public transportation.
- Sports: Distance vs time graphs are used to analyze the performance of athletes, including runners, swimmers, and cyclists.
Conclusion
In conclusion, distance vs time graphs are a powerful tool for analyzing the motion of objects. By understanding how to read and interpret these graphs, you can gain valuable insights into the world of physics and mathematics. Whether you are a student, teacher, or simply interested in learning more about distance vs time graphs, we hope this article has been informative and helpful.
Gallery of Distance vs Time Graphs:
Distance vs Time Graphs Image Gallery
We hope you have found this article informative and helpful. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to leave them in the section below.
