Intro
Discover the intricate mechanisms of a power plant in this in-depth exploration. Learn how electricity is generated, from fuel combustion to turbine rotation, and understand the crucial roles of boilers, generators, and transmission systems. Uncover the science behind power production and the innovations driving the industry forward, optimizing energy efficiency and sustainability.
The world of power plants is a fascinating one, filled with complex machinery, innovative technology, and a crucial role in meeting our daily energy needs. As we continue to rely on electricity to power our homes, businesses, and industries, it's essential to understand the inner workings of a power plant. In this article, we'll delve into the different types of power plants, their components, and the processes that generate the electricity that powers our lives.

Types of Power Plants
There are several types of power plants, each with its own unique characteristics and advantages. The most common types of power plants include:
- Thermal Power Plants: These plants generate electricity by burning fossil fuels such as coal, natural gas, or oil. The heat produced from burning these fuels is used to produce steam, which drives a turbine to generate electricity.
- Nuclear Power Plants: These plants use nuclear reactions to generate steam, which drives a turbine to produce electricity.
- Hydroelectric Power Plants: These plants harness the energy of moving water to generate electricity. Water from a dam or river is channeled through a turbine, which drives a generator to produce electricity.
- Renewable Energy Power Plants: These plants generate electricity from renewable sources such as solar, wind, and geothermal energy.
Components of a Power Plant
A typical power plant consists of several key components, including:
- Boiler: This is the heart of a power plant, where fuel is burned to produce heat.
- Turbine: This is a mechanical device that converts the heat energy produced in the boiler into mechanical energy.
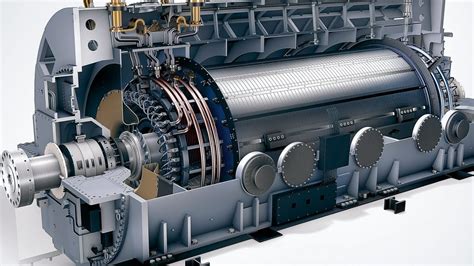
- Generator: This is a machine that converts the mechanical energy produced by the turbine into electrical energy.
- Transformer: This is a device that increases or decreases the voltage of the electrical energy produced by the generator.
- Transmission Lines: These are the power lines that carry the electrical energy from the power plant to the consumer.
The Process of Generating Electricity
The process of generating electricity in a power plant involves several stages:
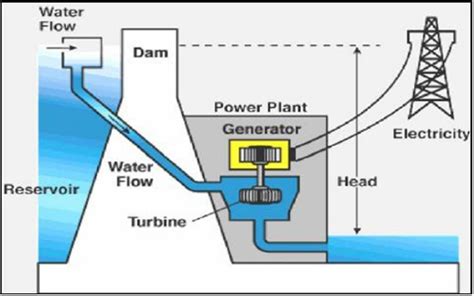
- Fuel Handling: The fuel used to generate electricity is transported to the power plant and stored in a fuel handling system.
- Boiler Operation: The fuel is burned in the boiler to produce heat.
- Steam Generation: The heat produced in the boiler is used to produce steam.
- Turbine Operation: The steam produced in the boiler drives a turbine, which converts the heat energy into mechanical energy.
- Generator Operation: The mechanical energy produced by the turbine drives a generator, which converts the mechanical energy into electrical energy.
- Transformer Operation: The electrical energy produced by the generator is increased or decreased in voltage by a transformer.
- Transmission: The electrical energy is transmitted to the consumer through transmission lines.
Efficiency and Environmental Impact
Power plants have a significant impact on the environment, and their efficiency plays a crucial role in reducing this impact. The efficiency of a power plant is measured by its ability to convert the energy input into electrical energy output. The most efficient power plants are those that use combined-cycle technology, which can achieve efficiencies of up to 60%.

However, even the most efficient power plants produce emissions that contribute to climate change and air pollution. To reduce these emissions, power plants are implementing new technologies such as carbon capture and storage, and renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power.
Renewable Energy and the Future of Power Plants
The future of power plants is shifting towards renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power. These sources of energy are cleaner and more sustainable than traditional fossil fuels, and they are becoming increasingly cost-competitive.
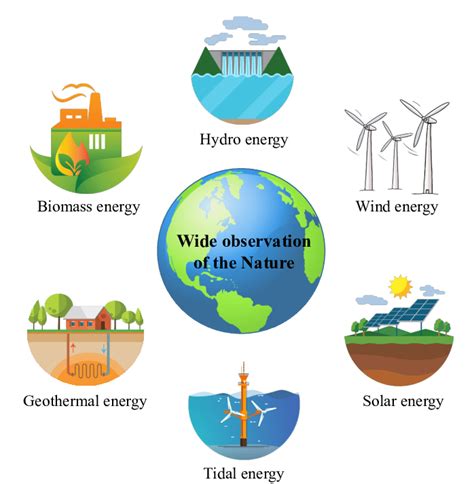
As the world continues to transition towards a low-carbon economy, power plants will play a crucial role in meeting our energy needs while reducing our environmental impact. Whether it's through traditional fossil fuels or renewable energy sources, the inner workings of a power plant will remain a vital part of our daily lives.
Power Plant Image Gallery








We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the inner workings of a power plant. Whether you're a student, engineer, or simply someone interested in learning more about the world of power plants, we encourage you to share your thoughts and questions in the comments below.
