Intro
Discover the pivotal role of nuclear weapons in the Cold War era. Learn about the arms race, nuclear deterrence, and iconic events like the Cuban Missile Crisis. Explore the strategic implications of nuclear proliferation, disarmament, and the balance of power between the US and Soviet Union, shaping global politics forever.
The Cold War era, which lasted from the end of World War II in 1945 to the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991, was marked by a decades-long period of tension and competition between the United States and the Soviet Union. One of the most significant aspects of this era was the development and proliferation of nuclear weapons, which played a crucial role in shaping the geopolitics of the time.
The development of nuclear weapons began in the early 1940s, when the United States launched the Manhattan Project, a secret research and development project aimed at creating an atomic bomb. The project was led by a team of scientists, including J. Robert Oppenheimer and Enrico Fermi, who worked tirelessly to develop a nuclear reactor and a uranium-based bomb. On August 6 and 9, 1945, the United States dropped atomic bombs on the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, respectively, killing hundreds of thousands of people and bringing an end to World War II.

The Soviet Union, which had been working on its own nuclear program, detonated its first atomic bomb in 1949. This marked the beginning of a nuclear arms race between the two superpowers, with both countries investing heavily in the development of more advanced nuclear weapons and delivery systems.
Nuclear Deterrence and the Balance of Power
The concept of nuclear deterrence, which holds that the possession of nuclear weapons can prevent an enemy from launching a nuclear attack, became a central component of Cold War strategy. Both the United States and the Soviet Union developed massive nuclear arsenals, with the United States maintaining a significant advantage in terms of the number and sophistication of its nuclear warheads.

The balance of power between the two superpowers was maintained through a delicate dance of diplomacy, military build-ups, and proxy wars. The United States and its allies formed the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), while the Soviet Union and its allies formed the Warsaw Pact. This bipolar world order was marked by a series of crises, including the Berlin Blockade, the Korean War, and the Cuban Missile Crisis, which brought the world to the brink of nuclear war.
The Role of Nuclear Weapons in the Cuban Missile Crisis
The Cuban Missile Crisis, which took place in October 1962, was the closest the world came to nuclear war during the Cold War era. The crisis began when the Soviet Union, under the leadership of Nikita Khrushchev, decided to deploy nuclear-armed ballistic missiles in Cuba, just 90 miles from the United States.
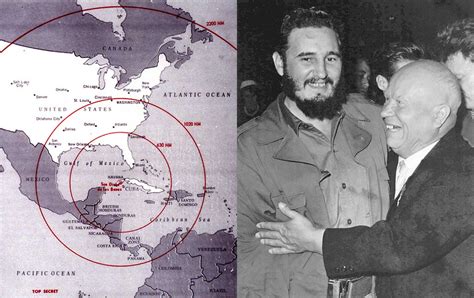
The United States, under the leadership of President John F. Kennedy, responded by imposing a naval quarantine on Cuba and threatening to invade the island if the Soviet Union did not withdraw its missiles. After a tense 13-day standoff, the Soviet Union agreed to withdraw its missiles in exchange for a U.S. promise not to invade Cuba and the removal of U.S. Jupiter missiles from Turkey.
The Impact of Nuclear Weapons on International Relations
The development and proliferation of nuclear weapons had a profound impact on international relations during the Cold War era. The threat of nuclear war led to a series of diplomatic efforts aimed at reducing the risk of nuclear conflict, including the Partial Test Ban Treaty, the Strategic Arms Limitation Talks (SALT), and the Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces Treaty (INF).

The possession of nuclear weapons also had a profound impact on the international non-proliferation regime, with the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT) being signed in 1968. The NPT, which has been ratified by almost 200 countries, aims to prevent the spread of nuclear weapons and promote disarmament.
The Legacy of Nuclear Weapons in the Cold War Era
The legacy of nuclear weapons in the Cold War era is complex and multifaceted. On the one hand, the possession of nuclear weapons played a significant role in maintaining the balance of power and preventing a large-scale conventional war between the superpowers. On the other hand, the threat of nuclear war had a profound impact on international relations, leading to a series of diplomatic efforts aimed at reducing the risk of nuclear conflict.

In conclusion, nuclear weapons played a significant role in the Cold War era, shaping the geopolitics of the time and influencing international relations. The development and proliferation of nuclear weapons led to a series of diplomatic efforts aimed at reducing the risk of nuclear conflict, and the legacy of nuclear weapons continues to shape international relations today.
Gallery of Cold War Era Nuclear Weapons
Cold War Era Nuclear Weapons Image Gallery










FAQ
Q: What was the significance of the Cuban Missile Crisis? A: The Cuban Missile Crisis was a major Cold War event in which the United States and the Soviet Union came close to nuclear war over the presence of Soviet nuclear-armed ballistic missiles in Cuba.
Q: What was the impact of nuclear weapons on international relations during the Cold War era? A: The possession of nuclear weapons had a profound impact on international relations, leading to a series of diplomatic efforts aimed at reducing the risk of nuclear conflict.
Q: What was the legacy of nuclear weapons in the Cold War era? A: The legacy of nuclear weapons in the Cold War era is complex and multifaceted, with both positive and negative consequences for international relations.
Q: What was the significance of the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty? A: The Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty, signed in 1968, aims to prevent the spread of nuclear weapons and promote disarmament.
Q: What was the impact of nuclear deterrence theory on international relations? A: Nuclear deterrence theory, which holds that the possession of nuclear weapons can prevent an enemy from launching a nuclear attack, played a significant role in maintaining the balance of power during the Cold War era.
