Discover the 5 crucial factors that determine carrying capacity in various environments. Learn how population growth, resource availability, and environmental limitations impact the delicate balance between humans, wildlife, and ecosystems. Understand the importance of carrying capacity in conservation, sustainability, and ecological management, and how it affects biodiversity and environmental resilience.
Carrying capacity is a crucial concept in environmental science and sustainability, referring to the maximum number of individuals of a species that an environment can support indefinitely. The carrying capacity of an ecosystem is determined by various factors, which can be broadly categorized into five key elements. Understanding these factors is essential for managing natural resources, conserving biodiversity, and ensuring sustainable development.
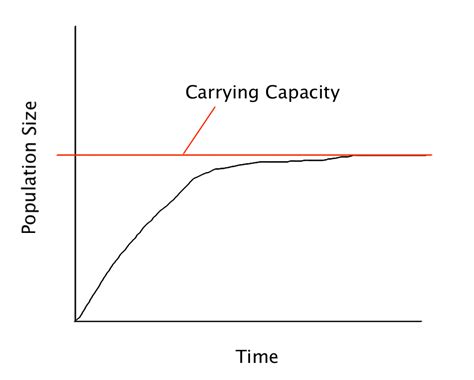
1. Food Availability
Food availability is a critical factor in determining carrying capacity. The amount of food available in an ecosystem can support a certain number of individuals. If the food supply is abundant, the carrying capacity of the ecosystem will be higher. Conversely, if food is scarce, the carrying capacity will be lower. For example, a forest ecosystem with an abundance of vegetation can support a larger population of herbivores, such as deer, than a forest with limited vegetation.
Factors Affecting Food Availability
Several factors can affect food availability, including:
- Climate: Climate conditions, such as temperature and precipitation, can impact the growth and productivity of plants, which in turn affect the availability of food for herbivores.
- Soil quality: The quality of the soil can impact the growth and productivity of plants, which can affect the availability of food for herbivores.
- Water availability: Access to water can impact the growth and productivity of plants, which can affect the availability of food for herbivores.
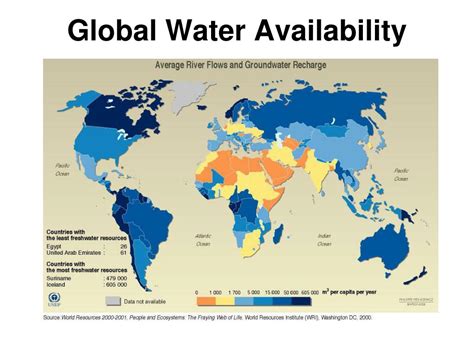
2. Water Availability
Water availability is another crucial factor in determining carrying capacity. Access to clean water is essential for the survival of most species. Ecosystems with limited water availability, such as deserts, have a lower carrying capacity than ecosystems with abundant water availability, such as rivers and lakes.

Factors Affecting Water Availability
Several factors can affect water availability, including:
- Climate: Climate conditions, such as precipitation and temperature, can impact the availability of water in an ecosystem.
- Geology: The geology of an ecosystem can impact the availability of water. For example, areas with impermeable rocks may have limited water availability.
- Human activities: Human activities, such as water pollution and over-extraction, can impact the availability of clean water in an ecosystem.
3. Shelter and Habitat
Shelter and habitat are essential for the survival of most species. Ecosystems with limited shelter and habitat, such as urban areas, have a lower carrying capacity than ecosystems with abundant shelter and habitat, such as forests and grasslands.

Factors Affecting Shelter and Habitat
Several factors can affect shelter and habitat, including:
- Climate: Climate conditions, such as temperature and precipitation, can impact the quality and availability of shelter and habitat.
- Geology: The geology of an ecosystem can impact the quality and availability of shelter and habitat. For example, areas with rocky terrain may have limited shelter and habitat.
- Human activities: Human activities, such as deforestation and urbanization, can impact the quality and availability of shelter and habitat.
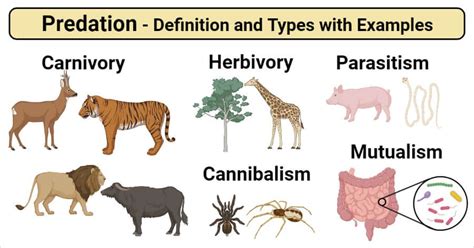
4. Predation and Disease
Predation and disease can impact the carrying capacity of an ecosystem. Predators can regulate the population size of prey species, while disease can impact the survival and reproduction of individuals.
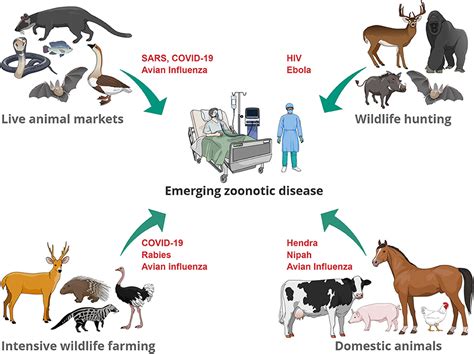
Factors Affecting Predation and Disease
Several factors can affect predation and disease, including:
- Climate: Climate conditions, such as temperature and precipitation, can impact the prevalence and severity of disease.
- Habitat quality: The quality of the habitat can impact the prevalence and severity of disease. For example, areas with poor habitat quality may have higher disease prevalence.
- Human activities: Human activities, such as overhunting and habitat destruction, can impact the prevalence and severity of disease.
5. Human Impact
Human impact is a significant factor in determining carrying capacity. Human activities, such as overfishing, overhunting, and habitat destruction, can impact the carrying capacity of an ecosystem.

Factors Affecting Human Impact
Several factors can affect human impact, including:
- Population size: The size of the human population can impact the carrying capacity of an ecosystem. Larger populations tend to have a greater impact on the environment.
- Technology: The level of technology can impact the carrying capacity of an ecosystem. For example, the development of fishing gear can impact the population size of fish species.
- Economic activities: Economic activities, such as agriculture and mining, can impact the carrying capacity of an ecosystem.
Carrying Capacity Image Gallery






In conclusion, the carrying capacity of an ecosystem is determined by a complex interplay of factors, including food availability, water availability, shelter and habitat, predation and disease, and human impact. Understanding these factors is essential for managing natural resources, conserving biodiversity, and ensuring sustainable development. By recognizing the limitations of our planet's resources, we can work towards creating a more sustainable future for all species.
We invite you to share your thoughts on carrying capacity and its importance in the comments below. How do you think we can work towards creating a more sustainable future?
