Intro
Discover how alcohol impacts Celsius, a popular energy drink, and learn about the 5 ways it affects calorie burn, metabolism, and weight loss, including interactions with ingredients like caffeine and vitamins.
Alcohol consumption has become a widespread phenomenon globally, with many people indulging in it for various reasons, including socializing, relaxation, and coping with stress. However, it is essential to understand the effects of alcohol on our bodies, particularly when it comes to temperature regulation. Celsius, being a unit of temperature, is often used to measure the impact of alcohol on the body's thermal balance. In this article, we will delve into the ways alcohol affects Celsius, exploring the intricacies of this complex relationship.
The human body is designed to maintain a stable internal temperature, typically around 37°C (98.6°F). This process is crucial for optimal bodily functions, including metabolism, nerve function, and muscle activity. However, when alcohol is introduced into the system, it can disrupt this delicate balance, leading to fluctuations in body temperature. These changes can have significant consequences, ranging from mild discomfort to life-threatening conditions. As we explore the effects of alcohol on Celsius, it is vital to consider the broader implications of these changes on our overall health and well-being.
Alcohol's impact on body temperature is multifaceted, involving various physiological mechanisms that can either increase or decrease Celsius readings. For instance, alcohol can cause blood vessels to dilate, leading to increased blood flow to the skin's surface, which can result in a temporary drop in body temperature. Conversely, alcohol can also interfere with the body's ability to regulate its internal temperature, leading to hypothermia or hyperthermia in extreme cases. Understanding these complex interactions is crucial for appreciating the potential risks associated with alcohol consumption, particularly in situations where temperature regulation is critical, such as in extreme weather conditions or during intense physical activity.
Introduction to Alcohol's Effects on Body Temperature
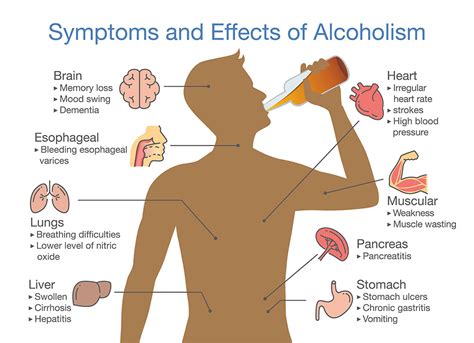
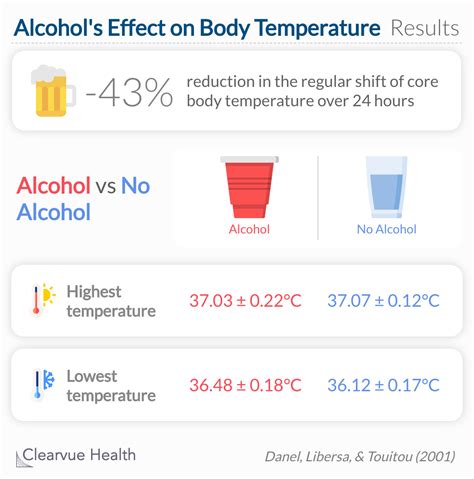
The relationship between alcohol and Celsius is intricate, with various factors influencing the outcome. These factors include the amount and type of alcohol consumed, individual tolerance, and environmental conditions. It is essential to recognize that alcohol's effects on body temperature can vary significantly from person to person, making it challenging to predict the exact outcome. Nevertheless, by examining the general trends and mechanisms involved, we can better comprehend the potential risks and consequences of alcohol consumption on our thermal balance.
5 Ways Alcohol Affects Celsius

The following sections will outline the five primary ways in which alcohol affects Celsius, providing a detailed analysis of the underlying physiological mechanisms and potential consequences.
1. Vasodilation and Heat Loss
Alcohol consumption causes blood vessels to dilate, leading to increased blood flow to the skin's surface. This process, known as vasodilation, can result in a temporary drop in body temperature as heat is lost more efficiently. While this effect may seem beneficial in warm environments, it can be detrimental in cold conditions, where the body's ability to retain heat is crucial for survival.2. Impaired Thermoregulation
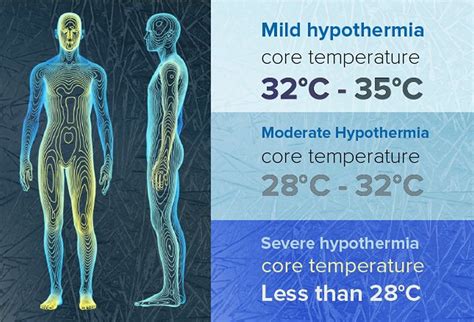
Alcohol can interfere with the body's natural thermoregulatory mechanisms, making it more challenging to maintain a stable internal temperature. This impairment can lead to hypothermia (abnormally low body temperature) or hyperthermia (abnormally high body temperature), both of which can have severe consequences, including organ damage and even death.3. Dehydration and Heat Retention
Alcohol is a diuretic, meaning it increases urine production and can lead to dehydration if not balanced with sufficient fluid intake. Dehydration can impair the body's ability to regulate its temperature, as sweat evaporation is a crucial mechanism for cooling. In dehydrated states, the body may retain heat more efficiently, leading to increased Celsius readings and potential heat-related illnesses.4. Metabolic Changes
Alcohol consumption can alter metabolic rates, affecting the body's energy production and heat generation. While alcohol itself contains calories, its metabolism can lead to increased heat production, potentially raising body temperature. However, this effect can be offset by the decreased metabolic rate associated with chronic alcohol consumption, which may lead to weight loss and reduced thermal insulation.5. Hormonal Influences
Alcohol can influence various hormonal pathways, including those involved in thermoregulation. For example, alcohol can affect the release of thyroid hormones, which play a crucial role in regulating metabolism and heat production. Changes in these hormonal balances can have significant effects on body temperature, either increasing or decreasing Celsius readings depending on the specific hormonal responses.Practical Considerations and Precautions

Given the complex and potentially hazardous effects of alcohol on Celsius, it is essential to approach alcohol consumption with caution. This includes being aware of the amount and type of alcohol consumed, as well as individual tolerance and environmental conditions. Additionally, it is crucial to maintain adequate hydration, avoid extreme temperatures, and seek medical attention if symptoms of hypothermia or hyperthermia occur.
Statistical Insights and Research Findings
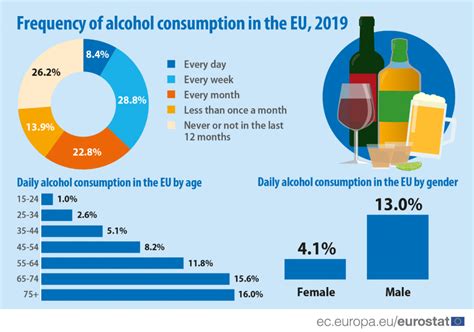
Numerous studies have investigated the relationship between alcohol consumption and body temperature, providing valuable insights into the mechanisms and consequences involved. These findings highlight the importance of responsible alcohol consumption and the need for increased awareness about the potential risks associated with alcohol's effects on Celsius.
Gallery of Alcohol and Temperature Regulation
Alcohol and Temperature Regulation Image Gallery
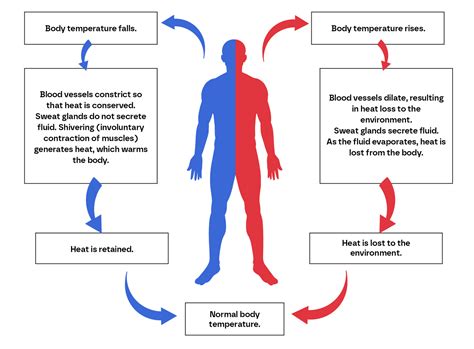
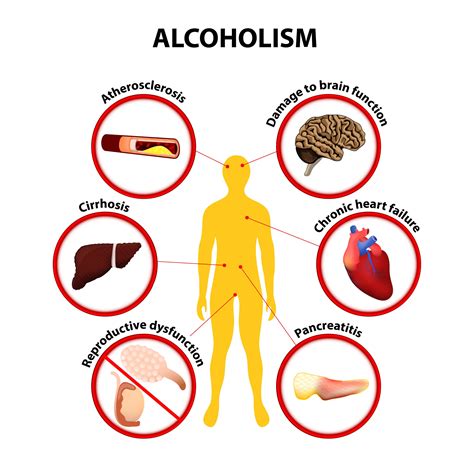




Final Thoughts and Recommendations

In conclusion, the relationship between alcohol and Celsius is complex and multifaceted, involving various physiological mechanisms that can either increase or decrease body temperature. By understanding these effects and taking necessary precautions, individuals can enjoy alcohol responsibly while minimizing the risks associated with its consumption. We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences on this topic, and we encourage everyone to prioritize their health and well-being by being mindful of the potential consequences of alcohol consumption on their thermal balance. Please feel free to comment, share this article, or take specific actions to promote responsible drinking practices and raise awareness about the importance of temperature regulation in the context of alcohol consumption.
