Intro
Discover the Combat Medic Army pay scale and benefits. Learn about the salary range, allowances, and bonuses for 68W Combat Medics. Explore the education, training, and certification benefits, as well as special pays and incentives. Get the inside scoop on the compensation package for these critical healthcare professionals in the US Army.
The role of a Combat Medic in the US Army is a vital one, requiring a unique blend of medical expertise and combat readiness. As a Combat Medic, you will be responsible for providing medical care to fellow soldiers in the midst of battle, often in high-stress and high-risk environments. In this article, we'll delve into the details of the Combat Medic Army pay scale and benefits, as well as the rewards and challenges of this esteemed profession.
What Does a Combat Medic Do?

A Combat Medic is a specialized soldier who has received advanced training in medical procedures and emergency care. Their primary responsibility is to provide medical care to fellow soldiers in combat zones, often in situations where medical resources are limited. This may involve treating wounds, administering medication, and stabilizing patients for evacuation to a medical facility.
In addition to their medical duties, Combat Medics may also be responsible for providing basic life support, including CPR and first aid. They may also assist with medical evacuations, communicate with medical personnel, and maintain medical records.
Combat Medic Army Pay Scale
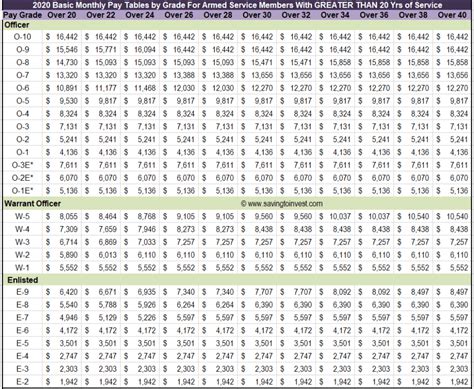
The pay scale for Combat Medics in the US Army is based on rank and time in service. The Army uses a tiered pay system, with higher ranks and longer service times corresponding to higher pay levels.
Here is a rough outline of the Combat Medic Army pay scale:
- Private (E-1): $1,733 - $2,054 per month
- Private First Class (E-2): $1,942 - $2,344 per month
- Specialist/Corporal (E-4): $2,448 - $3,044 per month
- Sergeant (E-5): $2,804 - $3,442 per month
- Staff Sergeant (E-6): $3,231 - $4,044 per month
- Sergeant First Class (E-7): $3,643 - $4,566 per month
- Master Sergeant/First Sergeant (E-8): $4,047 - $5,047 per month
- Sergeant Major (E-9): $4,514 - $5,571 per month
Keep in mind that these figures are subject to change and do not include additional forms of compensation, such as hazard pay and bonuses.
Combat Medic Benefits
In addition to their pay, Combat Medics receive a range of benefits, including:
- Comprehensive medical and dental care
- Access to on-base facilities, including gyms, swimming pools, and libraries
- Education benefits, including tuition assistance and the GI Bill
- Housing and food allowances
- Specialized training and certifications
- Opportunities for advancement and promotion
How to Become a Combat Medic

To become a Combat Medic, you will need to meet the Army's basic eligibility requirements, including:
- Being a US citizen
- Being between the ages of 17 and 35
- Having a high school diploma or equivalent
- Scoring a minimum of 110 on the Army's General Technical (GT) aptitude test
- Completing Basic Combat Training (BCT)
- Completing Advanced Individual Training (AIT) as a Combat Medic
The Combat Medic training program is highly competitive and requires a minimum of 16 weeks of training. This training includes:
- Basic life support and first aid
- Trauma care and wound management
- Pharmacology and medication administration
- Medical procedures and protocols
- Combat skills and tactics
Challenges and Rewards of Being a Combat Medic

Being a Combat Medic is an extremely challenging and rewarding profession. Some of the challenges include:
- Working in high-stress and high-risk environments
- Dealing with traumatic injuries and illnesses
- Making life-or-death decisions in emergency situations
- Maintaining physical and mental stamina in the face of prolonged combat operations
Despite these challenges, many Combat Medics report a high sense of job satisfaction and personal fulfillment. Some of the rewards include:
- Saving lives and making a positive impact on fellow soldiers
- Developing advanced medical skills and expertise
- Being part of a tight-knit community of medical professionals
- Serving their country and contributing to national defense
Combat Medic Specializations

Combat Medics can specialize in a range of areas, including:
- Tactical Combat Casualty Care (TCCC)
- Pre-Hospital Trauma Life Support (PHTLS)
- Advanced Trauma Life Support (ATLS)
- Critical Care Paramedicine
- Flight Medic
These specializations can provide additional training and certifications, as well as opportunities for advancement and promotion.
Combat Medic Career Progression

Combat Medics can progress through the ranks, from Private to Sergeant Major, as they gain experience and complete additional training and certifications. Here is a rough outline of the Combat Medic career progression:
- Private (E-1): New recruit
- Private First Class (E-2): Basic life support and first aid
- Specialist/Corporal (E-4): Advanced medical procedures and protocols
- Sergeant (E-5): Leadership and supervision
- Staff Sergeant (E-6): Senior leadership and mentorship
- Sergeant First Class (E-7): Advanced leadership and education
- Master Sergeant/First Sergeant (E-8): Senior leadership and administration
- Sergeant Major (E-9): Senior leadership and command
Combat Medic Education and Training

Combat Medics receive comprehensive education and training, including:
- Basic life support and first aid
- Trauma care and wound management
- Pharmacology and medication administration
- Medical procedures and protocols
- Combat skills and tactics
Combat Medics can also pursue additional education and certifications, such as:
- Bachelor's degree in nursing or a related field
- Master's degree in nursing or a related field
- Certification as a paramedic or registered nurse
- Certification in specialized areas, such as TCCC or PHTLS
Combat Medic Career Outlook

The career outlook for Combat Medics is highly positive, with opportunities for advancement and promotion within the Army. Combat Medics can also transition to civilian careers in medicine, such as nursing or paramedicine.
Here are some potential career paths for Combat Medics:
- Registered nurse
- Paramedic
- Emergency medical technician (EMT)
- Medical administrator
- Medical educator
Gallery of Combat Medic Images
Combat Medic Image Gallery








We hope this comprehensive guide to the Combat Medic Army pay scale and benefits has provided you with valuable insights into this esteemed profession. As a Combat Medic, you will have the opportunity to make a real difference in the lives of your fellow soldiers, while also developing advanced medical skills and expertise. If you are interested in pursuing a career as a Combat Medic, we encourage you to explore this rewarding and challenging profession further.
