Intro
Unlock the full potential of Excel with 10 essential Visual Basic tips. Master Excel VBA programming and automate tasks with ease. Discover how to write efficient code, manipulate data, and create interactive dashboards. Boost productivity and take your spreadsheet skills to the next level with these expert VBA tips and tricks.
Mastering Excel VBA is a valuable skill for anyone who wants to take their spreadsheet game to the next level. Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) is a powerful programming language that allows you to automate tasks, create custom tools, and manipulate data in Excel. In this article, we will share 10 essential Visual Basic tips to help you become an Excel VBA master.

Understanding the Basics of VBA
Before we dive into the tips, it's essential to understand the basics of VBA. VBA is a programming language that is used to create and automate tasks in Excel. It's a visual language, meaning you can create and edit code by using a visual interface. VBA is made up of variables, data types, operators, control structures, functions, and objects.
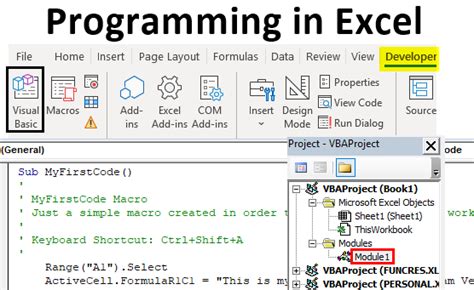
To get started with VBA, you need to open the Visual Basic Editor in Excel. To do this, press Alt + F11 or navigate to Developer > Visual Basic in the ribbon.
Tip 1: Declaring Variables
In VBA, variables are used to store and manipulate data. To declare a variable, you use the Dim statement. For example:
Dim myVariable As Integer
This declares a variable called myVariable as an integer data type.
Tip 2: Using Loops
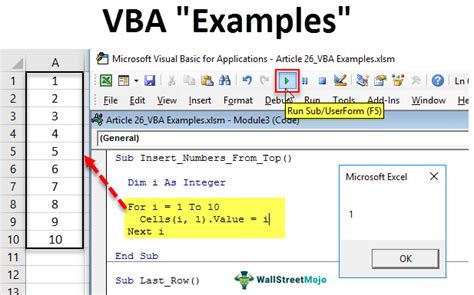
Loops are used to repeat a set of instructions. In VBA, you can use the For...Next loop or the Do...While loop. For example:
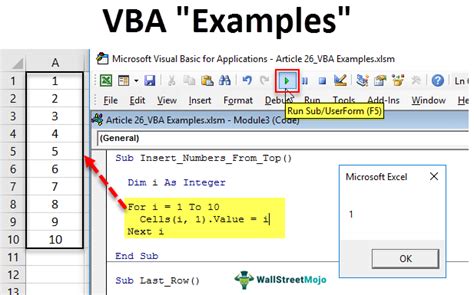
For i = 1 To 10 Cells(i, 1).Value = i Next i
This loop sets the value of each cell in the first column to the loop counter.

Working with Objects
In VBA, objects are used to represent elements in Excel, such as workbooks, worksheets, ranges, and charts.
Tip 3: Working with Workbooks
To work with workbooks, you can use the Workbooks object. For example:
Dim myWorkbook As Workbook Set myWorkbook = Workbooks.Open("C:\MyWorkbook.xlsx")
This opens a workbook called MyWorkbook.xlsx and assigns it to the myWorkbook variable.
Tip 4: Working with Worksheets
To work with worksheets, you can use the Worksheets object. For example:
Dim myWorksheet As Worksheet Set myWorksheet = myWorkbook.Worksheets("Sheet1")
This sets the myWorksheet variable to the first worksheet in the myWorkbook workbook.
Using Functions and Subroutines
Functions and subroutines are used to organize and reuse code in VBA.
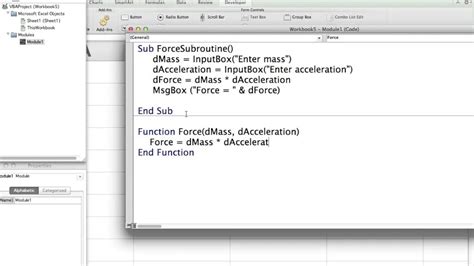
Tip 5: Creating Functions
To create a function, you can use the Function statement. For example:
Function AddNumbers(x As Integer, y As Integer) As Integer AddNumbers = x + y End Function
This creates a function called AddNumbers that takes two integer arguments and returns their sum.
Tip 6: Creating Subroutines
To create a subroutine, you can use the Sub statement. For example:
Sub Hello World() MsgBox "Hello, World!" End Sub
This creates a subroutine called Hello World that displays a message box with the text "Hello, World!".
Error Handling and Debugging
Error handling and debugging are essential skills in VBA programming.
Tip 7: Using On Error
To handle errors, you can use the On Error statement. For example:
On Error GoTo ErrorHandler
This redirects the program to the ErrorHandler label if an error occurs.
Tip 8: Using Debug.Print
To debug your code, you can use the Debug.Print statement. For example:
Debug.Print "The value of x is: " & x
This prints the value of the x variable to the Immediate window.

Best Practices and Tips
Here are a few best practices and tips to keep in mind when working with VBA:
Tip 9: Use Meaningful Variable Names
Use meaningful variable names to make your code easier to read and understand.
Tip 10: Use Comments
Use comments to explain your code and make it easier to understand.

Master Excel VBA Gallery
By following these 10 essential Visual Basic tips, you can become an Excel VBA master and take your spreadsheet skills to the next level. Remember to practice regularly, use meaningful variable names, and comment your code to make it easier to understand. Happy coding!
