Intro
Manage myocardial infarction effectively with the ATi template. Learn 6 evidence-based strategies to reduce morbidity and mortality rates. Discover how to assess, diagnose, and treat cardiac patients using the ATi template, incorporating key concepts like coronary artery disease, cardiac rehabilitation, and medication management for optimal outcomes.
Myocardial infarction, commonly known as a heart attack, is a serious medical condition that occurs when the blood flow to the heart is blocked, causing damage to the heart muscle. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), myocardial infarction is one of the leading causes of death worldwide. However, with proper management and treatment, it is possible to reduce the risk of complications and improve outcomes. In this article, we will discuss six ways to manage myocardial infarction using the Assessment, Technologies, Information, and Administration (ATI) template.

Assessment of Myocardial Infarction
Assessment is the first step in managing myocardial infarction. A thorough assessment helps healthcare professionals to identify the extent of the damage and develop an effective treatment plan. The assessment includes:
- Medical history: Assessing the patient's medical history, including any previous heart conditions, allergies, and medications.
- Physical examination: Performing a physical examination to check for signs of heart damage, such as abnormal heart sounds or rhythms.
- Laboratory tests: Conducting laboratory tests, such as electrocardiogram (ECG), blood tests, and imaging tests, to confirm the diagnosis and assess the extent of the damage.
Technologies for Myocardial Infarction Management
Several technologies are available to manage myocardial infarction, including:
1. Thrombolytic Therapy
Thrombolytic therapy involves administering medications to dissolve the blood clot that is blocking the blood flow to the heart. This therapy is most effective when administered within a few hours of the onset of symptoms.
2. Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI)
Primary PCI involves inserting a catheter through an artery in the leg or arm and guiding it to the blocked coronary artery. A balloon is then inflated to open the artery, and a stent is placed to keep the artery open.
3. Cardiac Rehabilitation
Cardiac rehabilitation is a program that helps patients recover from myocardial infarction and reduce the risk of future heart problems. The program includes exercise, education, and lifestyle modification.
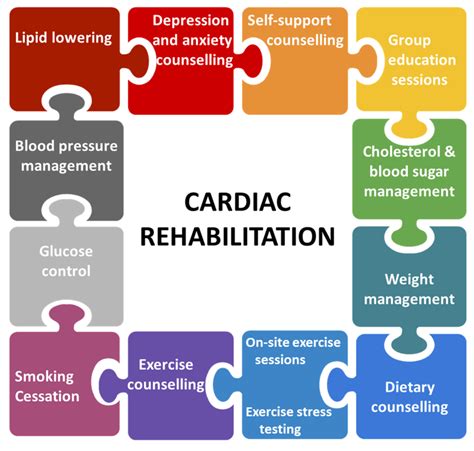
Information for Myocardial Infarction Management
Providing patients with accurate and timely information is crucial in managing myocardial infarction. Patients should be informed about:
- The causes and symptoms of myocardial infarction
- The treatment options and their benefits and risks
- The importance of lifestyle modification, such as quitting smoking, exercising regularly, and eating a healthy diet
- The need for regular follow-up appointments and monitoring
Administration of Myocardial Infarction Management
Effective administration is critical in managing myocardial infarction. This includes:
1. Developing a Treatment Plan
Developing a treatment plan that takes into account the patient's individual needs and medical history.
2. Coordinating Care
Coordinating care among healthcare professionals, including cardiologists, nurses, and other specialists.
3. Monitoring Progress
Monitoring the patient's progress and adjusting the treatment plan as needed.

Gallery of Myocardial Infarction Management
Myocardial Infarction Management Image Gallery








In conclusion, managing myocardial infarction requires a comprehensive approach that includes assessment, technologies, information, and administration. By following the six ways outlined in this article, healthcare professionals can provide effective care and improve outcomes for patients with myocardial infarction. We encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences on managing myocardial infarction in the comments section below.
