Intro
Discover a fresh approach to team collaboration with Joining In From The Back: A New Perspective. Learn how to effectively integrate new members, foster inclusive team dynamics, and boost collective productivity. Explore innovative strategies for seamless onboarding, overcoming communication barriers, and cultivating a culture of active participation and shared ownership.
In recent years, the world has witnessed a significant shift in the way we approach and think about various aspects of life. From technology to social justice, new perspectives have emerged, challenging traditional norms and sparking meaningful conversations. One such perspective is the concept of "joining in from the back," a phrase that has gained traction in various fields, including education, business, and social activism. In this article, we will delve into the meaning and significance of this concept, exploring its benefits, challenges, and potential applications.
What Does it Mean to Join In From the Back?
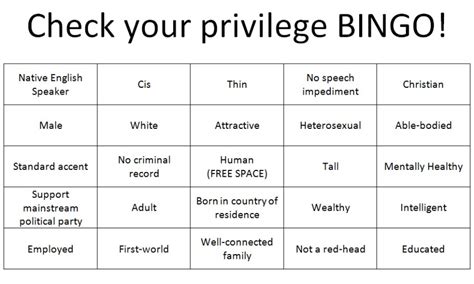
Joining in from the back refers to the act of participating in a group, community, or movement from a position of humility and openness. It involves acknowledging one's own limitations, biases, and privilege, and being willing to learn from others, particularly those who have been marginalized or excluded. This approach recognizes that traditional leadership models, which often prioritize dominant voices and perspectives, can be limiting and exclusionary. By joining in from the back, individuals can create space for others to take the lead, share their experiences, and contribute to the collective effort.
The Benefits of Joining In From the Back
The benefits of joining in from the back are numerous. For one, it allows individuals to build meaningful relationships with others, particularly those from diverse backgrounds and experiences. By listening and learning from others, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of the world and its complexities. Joining in from the back also promotes collaboration, creativity, and innovation, as individuals from different backgrounds and perspectives come together to share ideas and solve problems.
Moreover, joining in from the back can help to address issues of privilege, power, and oppression. By acknowledging and surrendering one's own privilege, individuals can create space for others to take the lead and share their experiences. This approach can help to dismantle systems of oppression and promote greater social justice.
Challenges and Critiques

While joining in from the back offers numerous benefits, it is not without its challenges and critiques. One of the primary challenges is the need for self-reflection and humility. Joining in from the back requires individuals to acknowledge their own limitations, biases, and privilege, which can be a difficult and uncomfortable process. Additionally, individuals may face resistance or skepticism from others, particularly those who are accustomed to traditional leadership models.
Critics of joining in from the back argue that it can be overly simplistic or naive, failing to account for the complexities of power dynamics and social structures. Others argue that it can be a form of "performative allyship," where individuals claim to be joining in from the back but ultimately maintain their privilege and dominance.
Addressing the Challenges and Critiques
To address the challenges and critiques of joining in from the back, it is essential to approach this concept with nuance and critical thinking. Individuals must be willing to engage in ongoing self-reflection and education, recognizing that joining in from the back is a continuous process rather than a one-time event.
Moreover, individuals must be aware of the power dynamics and social structures that shape our world. Joining in from the back is not a panacea for social justice, but rather one strategy among many that can help to promote greater equity and inclusion.
Applications and Examples

Joining in from the back has numerous applications across various fields, including education, business, and social activism. In education, joining in from the back can involve teachers creating space for students to take the lead in discussions and decision-making processes. In business, it can involve executives and managers stepping back to allow others to contribute to meetings and decision-making processes.
In social activism, joining in from the back can involve individuals from dominant groups stepping back to allow individuals from marginalized communities to take the lead in social justice movements. For example, during the Black Lives Matter movement, many white allies joined in from the back, allowing black leaders to take the lead in organizing protests and advocating for policy changes.
Conclusion and Call to Action
Joining in from the back is a powerful concept that has the potential to promote greater social justice, equity, and inclusion. While it is not without its challenges and critiques, this approach can help individuals to build meaningful relationships, promote collaboration and innovation, and address issues of privilege, power, and oppression.
As we move forward, it is essential that we approach this concept with nuance and critical thinking, recognizing that joining in from the back is a continuous process rather than a one-time event. We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences with joining in from the back, and to consider how they can apply this concept in their own lives and communities.
Joining In From The Back Image Gallery