Intro
Learn how to extract time from datetime in Excel with ease. Discover 5 simple methods to separate time from date, including using formulas, formatting, and Excel functions like HOUR, MINUTE, and SECOND. Master time extraction techniques and boost your spreadsheet productivity with these actionable tips and tricks.
Unlocking Time from Datetime in Excel: A Comprehensive Guide
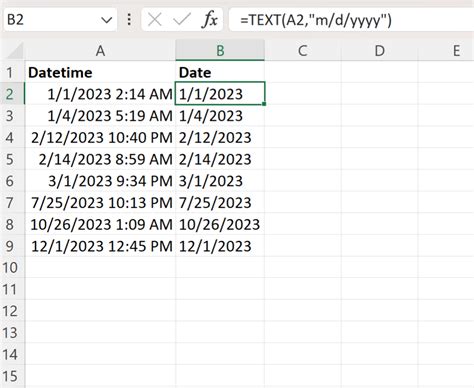
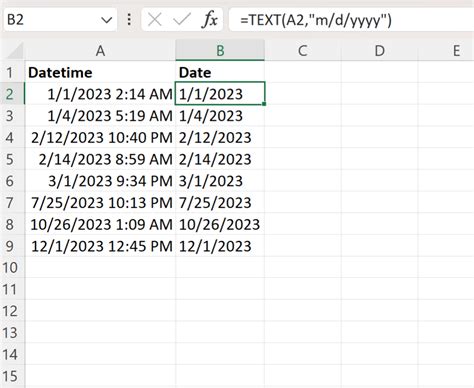
In the world of data analysis, working with datetime values is a common task. However, there are often situations where you need to extract the time component from a datetime value in Excel. This can be a challenge, especially for those new to Excel. In this article, we will explore five different methods to extract time from datetime in Excel, along with their applications and limitations.
Understanding Datetime in Excel
Before we dive into the methods, it's essential to understand how Excel stores datetime values. Excel represents datetime values as a single number, known as a serial number, which is a combination of the date and time. The date is stored as an integer, representing the number of days since January 1, 1900, while the time is stored as a decimal value, representing the fraction of a day.
Method 1: Using the HOUR, MINUTE, and SECOND Functions
One of the simplest ways to extract time from datetime in Excel is by using the HOUR, MINUTE, and SECOND functions. These functions extract the hour, minute, and second components from a datetime value, respectively.
Example: Extracting Time using HOUR, MINUTE, and SECOND
| Datetime | Hour | Minute | Second |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2022-01-01 08:30:00 | 8 | 30 | 0 |
Formula: =HOUR(A2), =MINUTE(A2), =SECOND(A2)
Where A2 is the cell containing the datetime value.
Method 2: Using the TEXT Function
Another way to extract time from datetime in Excel is by using the TEXT function. This function converts a datetime value to a text string, allowing you to extract the time component.
Example: Extracting Time using TEXT
| Datetime | Time |
|---|---|
| 2022-01-01 08:30:00 | 08:30:00 |
Formula: =TEXT(A2,"hh:mm:ss")
Where A2 is the cell containing the datetime value.
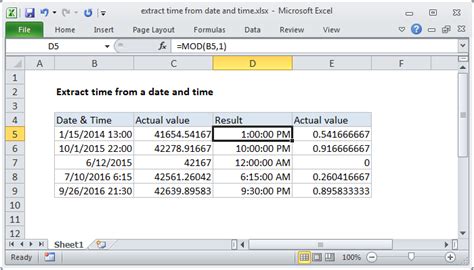
Method 3: Using the INT and MOD Functions
This method involves using the INT and MOD functions to extract the time component from a datetime value.
Example: Extracting Time using INT and MOD
| Datetime | Time |
|---|---|
| 2022-01-01 08:30:00 | 0.35417 |
Formula: =MOD(A2,1)
Where A2 is the cell containing the datetime value.
To convert this decimal value to a time, you can multiply it by 24.
Formula: =MOD(A2,1)*24
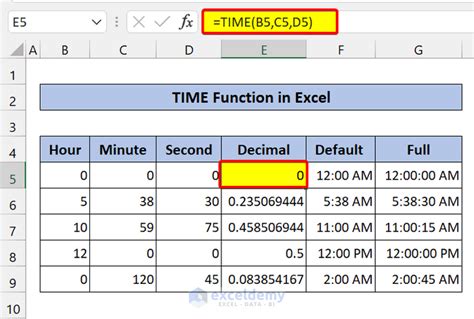
Method 4: Using the TIME Function
The TIME function is a simple way to extract the time component from a datetime value.
Example: Extracting Time using TIME
| Datetime | Time |
|---|---|
| 2022-01-01 08:30:00 | 08:30:00 |
Formula: =TIME(HOUR(A2),MINUTE(A2),SECOND(A2))
Where A2 is the cell containing the datetime value.
Method 5: Using Power Query
Power Query is a powerful tool in Excel that allows you to extract and transform data. You can use Power Query to extract the time component from a datetime value.
Example: Extracting Time using Power Query
| Datetime | Time |
|---|---|
| 2022-01-01 08:30:00 | 08:30:00 |
Formula: = DateTime.Time(DateTime.From([Datetime]))
Where [Datetime] is the column containing the datetime values.
Gallery of Excel Time Extraction
Excel Time Extraction Image Gallery
In conclusion, extracting time from datetime in Excel can be accomplished using various methods, each with its own strengths and limitations. By understanding the different techniques and formulas available, you can choose the best approach for your specific needs. Whether you're working with simple time extractions or complex datetime manipulations, Excel provides a range of tools and functions to help you achieve your goals.
